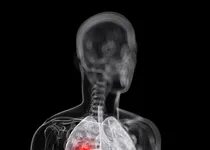
 Lung cancer is marked by unregulated cell growth in the lungs, resulting in cancerous tumors which frequently spread to other parts of the body. It is one of the most common and most deadly types of cancer. Causes include genetic predisposition, exposure to air pollution or airborne contaminants such as radon gas, and contact with asbestos. Smokers are at very high risk for contracting lung cancer. Tumors in the lungs are treated with chemotherapy, radiation therapy and, when possible, surgery. Removal of the affected lung may be possible, in cases where the tumor is localized on one side of the body.
Lung cancer is marked by unregulated cell growth in the lungs, resulting in cancerous tumors which frequently spread to other parts of the body. It is one of the most common and most deadly types of cancer. Causes include genetic predisposition, exposure to air pollution or airborne contaminants such as radon gas, and contact with asbestos. Smokers are at very high risk for contracting lung cancer. Tumors in the lungs are treated with chemotherapy, radiation therapy and, when possible, surgery. Removal of the affected lung may be possible, in cases where the tumor is localized on one side of the body.

