This kind of muscular dystrophy is somewhat different from some other variations of the condition—and it often doesn’t show up until adulthood. Also known as Steinert’s disease, it is “the most common form of adult-onset muscular dystrophy,” notes the Mayo Clinic.
No matter when the symptoms begin, they are usually marked by progressive muscle weakness, notes the source. Let’s have a closer look at seven facts about this condition that affects about 30,000 people in the United States…
1. It’s Hereditary
According to the Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation, this particular condition is inherited and is caused by a gene mutation that “prevents the gene from carrying out its function properly.” The severity of the symptoms worsens with each generation.
The source also explains that either parent with the mutated gene have a 50-percent chance of passing it on to their children, although the child will not develop the disease if neither parent has it. Meanwhile, a variation of the condition called congenital myotonic dystrophy (present at birth) is most often inherited from the mother.
2. It Can Appear in Middle Age
According to Muscular Dystrophy Canada, the adult-onset version of this disease can have no symptoms until age-40. That means patients could already have children by the time they realize they have the mutated gene.
The symptoms “vary widely from one person to the next, even among family members,” notes the source. The symptoms for adults usually include drooping facial muscles, weak neck muscles, and difficulty swallowing. Poor vision and weight loss can also be telltale signs.
3. It Affects the Ability to Relax Muscles
While muscle weakness is common with this condition, Muscular Dystrophy Canada also explains that another unique symptom is “myotonia”—which is trouble relaxing a muscle. This can be in addition to all the other symptoms.
That’s because myotonic dystrophy “is a very complex condition,” adds the source. It notes there are medications to treat the muscle stiffness (known as myotonia).
4. It Doesn’t Always Cause Disabilities
According to The Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA), the range of severity of symptoms among patients varies greatly. That means while some may develop some physical barriers, “ there are people with the disorder whose symptoms are so mild they hardly know anything is wrong.”
For the most part, there will be muscle weakness that develops “to the point of some disability,” adds the MDA. This can progress from the face and neck muscles down to the shoulders, hips and thighs, adds the source.
5. There are No Direct Treatments
The National Human Genome Research Institute says there is currently “no cure or specific treatment for myotonic dystrophy,” although there are some interventions that improve quality of life for patients.
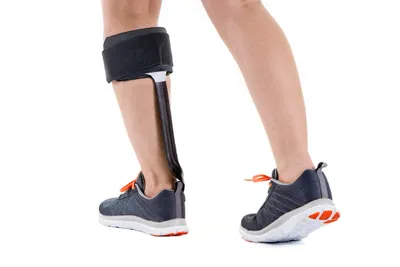
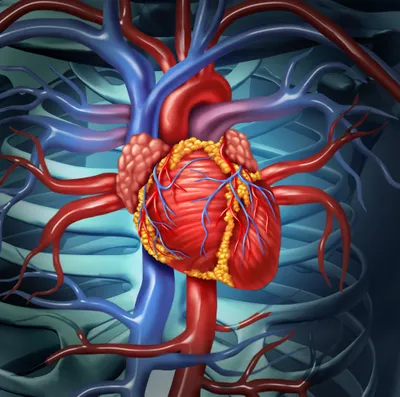
Those aids include ankle and leg supports or braces when muscle weakness progresses, adds the source. As mentioned before, medication can help loosen stiff muscles, while associated problems with the heart and eyes (cataracts) can be treated separately.
6. There’s a Milder Version
Myotonic dystrophy can be subdivided into two categories called DM1 and DM2, according to the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD). DM1 is a “multi-system” disorder that affects all skeletal muscles and in some cases the central nervous system.
Meanwhile, DM2 was once referred to as “ proximal myotonic myopathy” and has similar symptoms, adds the source. However, the symptoms tend to be milder “and more variable” than DM1.
7. Normal Lifespans are Possible among Patients
While symptoms can worsen over time, NORD notes that those with mild myotonic dystrophy can have a lifespan “in the normal range”. (The current average lifespan for American adults is 78-years).
However, those with “classic” myotonic dystrophy (DM1) can face a variety of physical problems that can affect cardiac function. The average lifespan for those with the classic version is 48 to 55-years, adds the source.