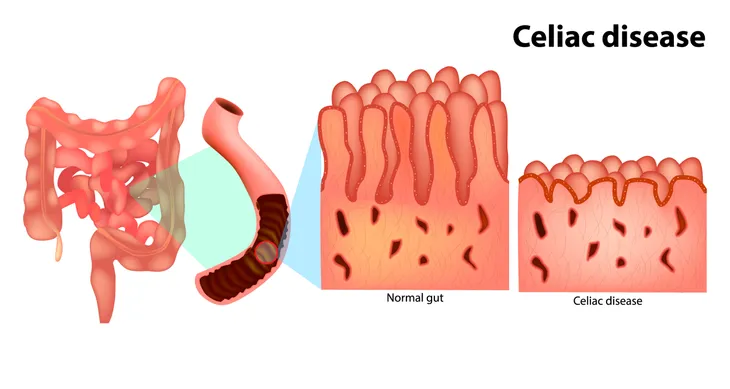
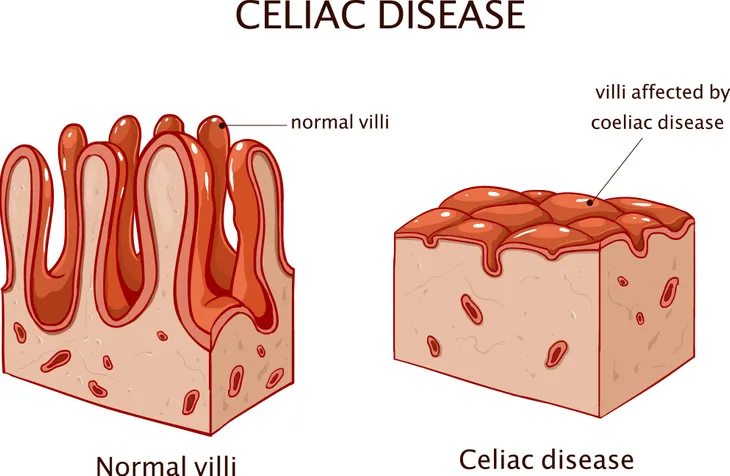
Celiac disease, also known as coeliac disease, is an autoimmune disorder that affects around 1 in 100 Americans. The disease is caused by gluten intolerance. Gliadin, a protein in wheat, causes the afflicted persons immune system to attack their own bowel tissue. This causes villous atrophy, or the erosion of the nutrient absorbing villi that line the small intestine. Other grains, such as barley and rye, have similarly shaped proteins that can cause the same reaction in sensitive individuals.
Celiac disease can cause irreversible damage. It is genetic in cause and can be passed down through generations. Testing for celiac disease is done through blood tests and endoscopy. It is important for the afflicted person to continue eating gluten while they are being tested for celiac disease. When they remove gluten from their diet, their body starts to repair itself, giving a false negative for the tests.
Celiac disease can cause a multitude of problems. The major ones come from the malabsorption of nutrients. This can lead to osteoporosis, anemia, and stunted growth in children. Those who suffer from celiac disease are also more likely to develop non-Hodgkin lymphoma when compared to the general population. The best way to protect yourself and minimize your risk is early diagnosis and strict diet.
Here are 15 symptoms of celiac disease. If you suffer from any of these symptoms or believe you may be at risk for celiac disease, please contact your doctor for testing.
1. No Symptoms
Unfortunately, many people who suffer from celiac disease have no symptoms. This is particularly dangerous, as intestinal damage can occur even when no symptoms are present. With new screening techniques, people are being diagnosed without ever suspecting they have the disease. It is important for people with no symptoms, but a positive diagnosis, to eat properly, as they are still at risk for serious complications of celiac disease, such as cancer.
2. Bloating
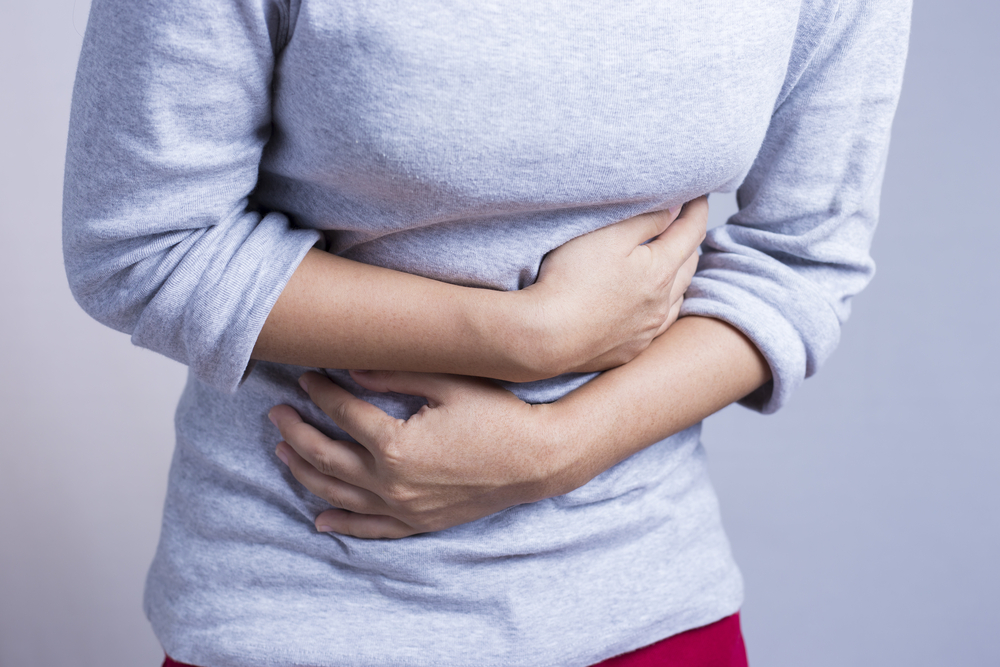
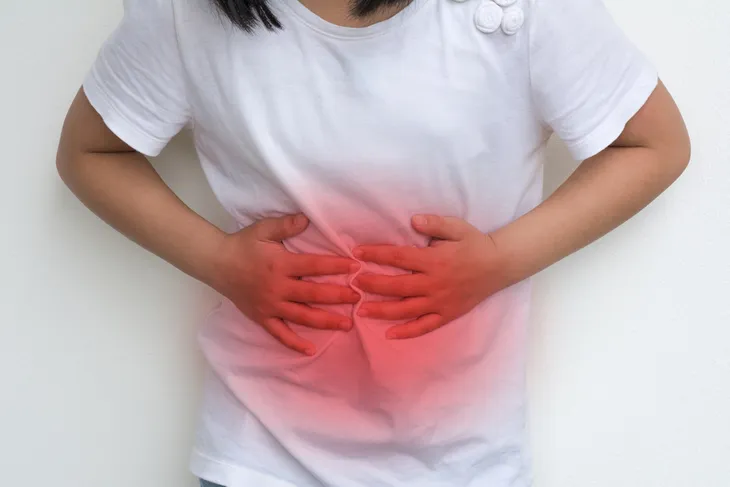
Many people who have celiac disease suffer from painful abdominal bloating. For days after consuming gluten, the stomach may be distended and filled with gas, which can be quite painful. Many people complain of intestinal pain and the feeling of being “6 months pregnant.” They may also suffer from excessive gas, or flatulence. Bloating can be a symptom of other dietary conditions, so look for it in conjunction with the consumption of gluten.
3. Diarrhea
Chronic diarrhea is a common symptom of those afflicted with celiac disease. The episodes may be smelly, explosive, and painful. The color of the stool may be pale or white and typically floats on the surface of the water. Even solid stools may present with these conditions. Symptoms related to chronic diarrhea include hemorrhoids. These can occur when there is not enough substance in the stools.
4. Constipation
While diarrhea is common in celiac sufferers, some people may be afflicted with constipation. This is from the body sluggishly moving the contents of the bowels. The body may be trying to pull all the nutrients possible from the food, as damaged villi will not work as efficiently. The constipation may be marked by periods of heavy diarrhea as the person consumes gluten. The constipation may cause pain and bloating.
5. Weight Loss or Gain
Many people who suffer from celiac disease lose weight as their body reacts to the missing nutrients. The diarrhea caused by gluten may stall the absorption of calories from food, purging the body of its fuel. Conversely, a sufferer may in fact gain weight instead of losing it. Their bodies may be screaming for nutrients, so they eat in excess to achieve proper nutrition. They may have a hard time losing weight until they restrict gluten from their diet.
6. Fatigue
Fatigue is a common complaint of those affected by celiac disease. Undiagnosed celiac sufferers may suffer from malnutrition caused by malabsorption issues. The body will respond with extreme fatigue and malaise. They may crave sugary foods and drink excessive caffeine just to stay energized. After diagnosis and the removal of gluten from the diet, fatigue may be the first symptom to be eliminated.
7. Trouble Concentrating
People who suffer from celiac disease may experience something called “brain fog” in relation to the consumption of gluten. This symptom occurs immediately after eating gluten and can persist for days. The feeling that it gives is confusion, trouble concentrating, and short-term memory loss. A sufferer may forget to pick their children up from school or even forget what they are writing mid-sentence. Thankfully, this symptom does not persist as a person removes gluten from their diet. It may even make them finally feel awake after years of fogginess.
8. Problems Falling and Staying Asleep
Recent studies have found that patients with celiac disease commonly suffer from disordered sleeping, even if the rest of their diet is healthy or not. Sleep disorders are more common to those suffering from celiac disease vs. the rest of the general population. The disordered sleeping can manifests as an inability to fall asleep or being unable to stay asleep. The study found that the causes of the inability to sleep well include depression, fatigue, and anxiety.
9. Numbness and Tingling
Many celiac sufferers exhibit nerve symptoms, such as numbness and tingling. Problems with the neurologic system can affect gross and fine motor control and sensory nerves. An undiagnosed celiac disease sufferer may find their extremities exhibit nerve problems. This can include a tingling sensation in the hands and feet, ranging from mild to “fallen asleep.” Conversely, they may not feel anything in their hands and feet, as numbness is a common complaint. Other parts of the body may be affected, such as the facial muscles and body nerves.
10. Depression
Unfortunately, depression and suicide rates are higher in people with celiac disease. Studies have found that, even with eating a gluten-free diet, the rates of depression in people with celiac disease are much higher than the general population. One study found a connection between disordered eating and depression in women who suffer from celiac disease. As they closely monitor their foods for gluten, disordered and restrictive eating can develop. For suicide risk, it seems that once diagnosed and with dietary changes, the suicide risk is greatly reduced.
11. Gas
After reading about some of the other symptoms on this list, gas probably shouldn’t be all that surprising! It often accompanies any stomach discomfort, such as bloating and diarrhea. Excess gas is a common symptoms of untreated celiac disease. Healthline even refers to a small study published in the Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology reiterating that gas is the most common symptom experienced by those with celiac disease.
The source also refers to another study that examined 96 adults, all of whom suffered from celiac disease and live in northern India. “Excess gas and bloating were present in 9.4-percent of cases,” writes Healthline.
It’s important to note that there are many different reasons a person might experience excess gas celiac disease is just one of them. “One study tested 150 people complaining of increased gas and found that only two tested positive for celiac disease,” explains the source. Other common causes are constipation, indigestion, swallowing air, and other conditions such as lactose intolerance and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
12. Iron Deficiency Anemia
Iron deficiency anemia occurs when there is a lack of red blood cells in the body. Celiac disease can sometimes lead to an iron deficiency, because it interferes with the body’s ability to absorb nutrients. “Symptoms of an iron deficiency anemia include fatigue, weakness, chest pain, headaches, and dizziness,” writes Healthline.
The source refers to one particular study that examined 34 children who have celiac disease. The evidence showed that nearly 15-percent also suffered from a mild to moderate form of iron deficiency anemia. Another study of 84 people “with iron deficiency anemia of an unknown origin found that 7-percent had celiac disease. After they went on a gluten-free diet, serum iron levels significantly increased,” explains Healthline.
The last study that Healthline refers to on this topic was published in the Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology that was performed on 727 celiac disease patients. According to the study, 23-percent of them were anemic, and those who were anemic, were twice as likely to have damage in their small intestine and a low bone mass. Both of these side effects were caused by celiac disease.
Again, there are many other reasons that a person can be suffering from iron deficiency anemia celiac disease isn’t the only cause. It can also be caused by a poor diet and long-term use of pain relievers like aspirin as well as a great deal of blood loss from heavy menstrual bleeding or peptic ulcers, says Healthline.
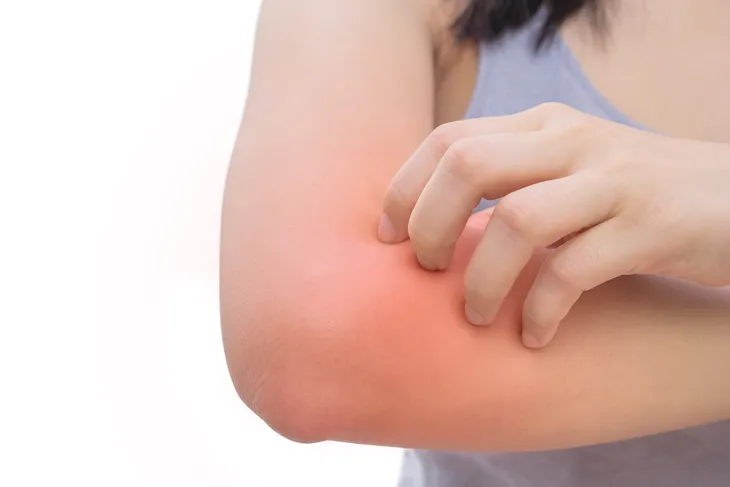
13. Itchy Rash
Celiac disease can sometimes cause an itchy rash, commonly referred to as dermatitis herpetiformis. This rash will cause a blistering irritation that tends to appear on the elbows, knees, or buttocks, says Healthline. According to a study published in the Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 17-percent of people with celiac disease experienced this type of rash, and in most cases, it is what leads their doctor to diagnose them with celiac disease. Healthline also notes that it could develop if they are not following their treatment properly.
“Interestingly enough, some people may develop this skin rash without the other digestive symptoms that typically occur with celiac disease. In fact, fewer than 10-percent of celiac patients who develop dermatitis herpetiformis experience digestive symptoms of celiac disease,” writes Healthline.
An itchy skin rash can also be caused by eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis, or hives.
14. Symptoms in Children
It’s not uncommon for children to have intestinal problems. In fact, WebMD points out that they are more common in children than they are in adults. When celiac disease does occur in a child or adult, it can cause an array of symptoms, including growth problems, weight loss, chronic diarrhea (that can even be bloody), constipation, vomiting, abdominal bloating and pain, fatigue, irritability, and failure to thrive, says the source.
A child with celiac disease might look like he or she is malnourished, with the telltale sign of a bloated abdomen. Their stomach will be distended but their thighs and buttocks will be flat.
15. Symptoms in Teens
Just as celiac disease can occur in children, infants, and adults, it can also occur in teenagers. WebMD points out that the symptoms of this condition are likely going to rear their ugly head when the teen is under a stressful situation, such as injury, leaving home, or pregnancy. Their symptoms will be similar to the ones we just listed for children, such as diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue, but will also include abdominal pain.
Other symptoms that might be present in teens that have not yet been listed are late puberty, growth problems, depression, itchy skin (dermatitis herpetiformis), or mouth sores, says WebMD.